[TOC]
向量
单位向量
-
单位向量=向量/向量长度
-
零矢量(即矢益的每个分量值都为 0, 如 v=(0,0,0)) 是不可以被归一化的。这是因为做除法 运算时分母不能为0
点积
-
公式: dot(a, b) = a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z;
-
用法特点:
-
可用于 计算投影
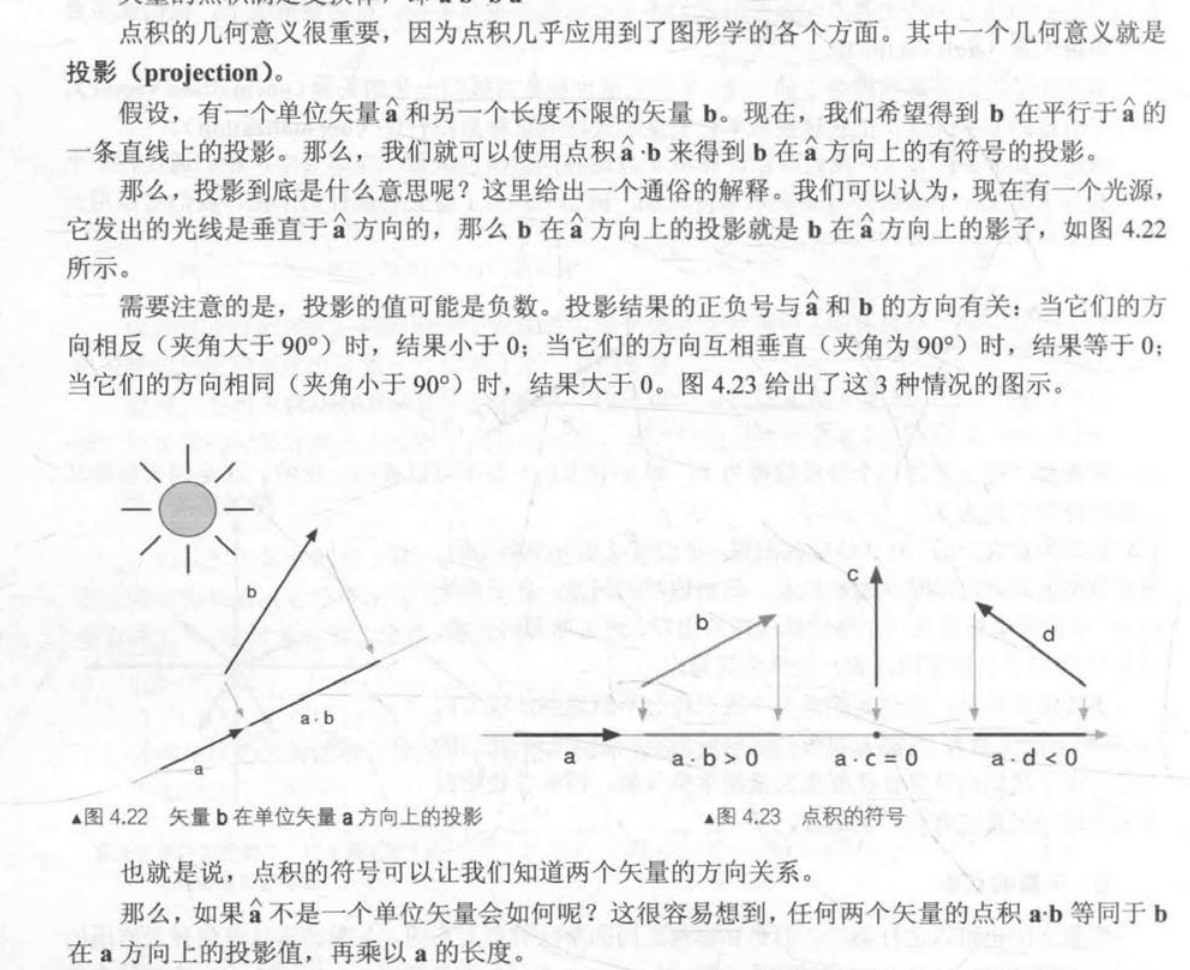
-
可以用于计算向量模的平方
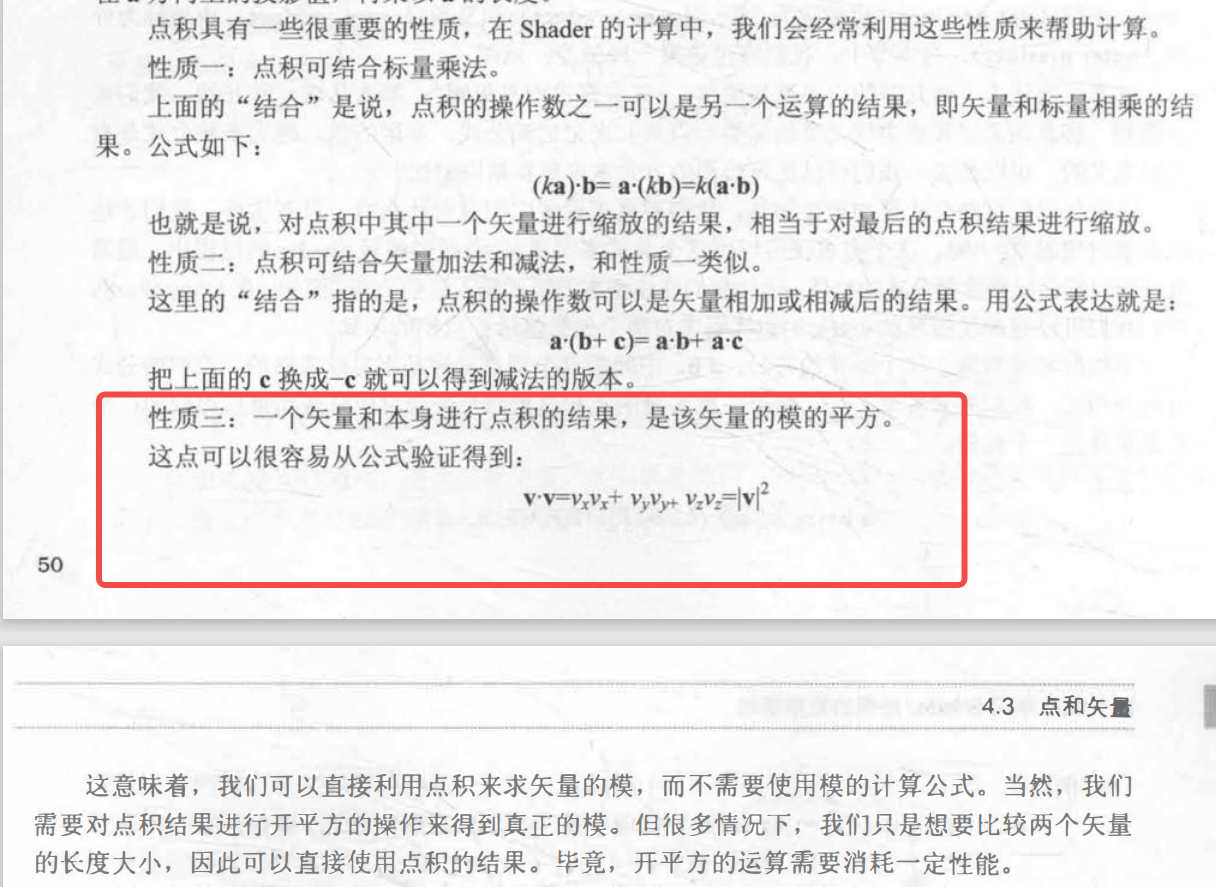
-
可以用于计算角度cos

-
叉积
公式:
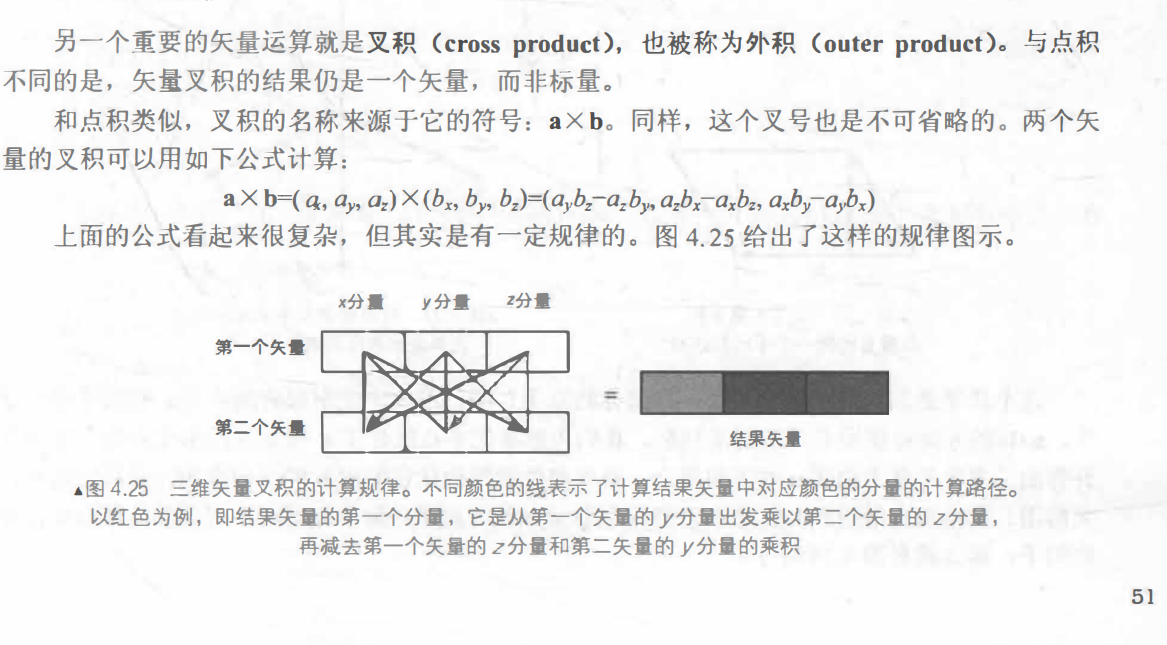
叉积到底有什么用呢?最常见的一个应用就是计算垂直于一个平面、 三角形的矢量。 另外, 还可以用于判断三角面片的朝向。
叉积的长度等于点积 的模的乘积再乘以它们之间夹角的正弦值

叉积的长度等于平行四边形的面积

叉积判断方向

光照模型 Blinn-Phong
- 漫反射
- 高光反射
- 自发光
- 环境光
漫反射
漫反射 = (物体颜色 * 灯光颜色) * max(0, dot(法线方向, 灯光方向))
高光反射
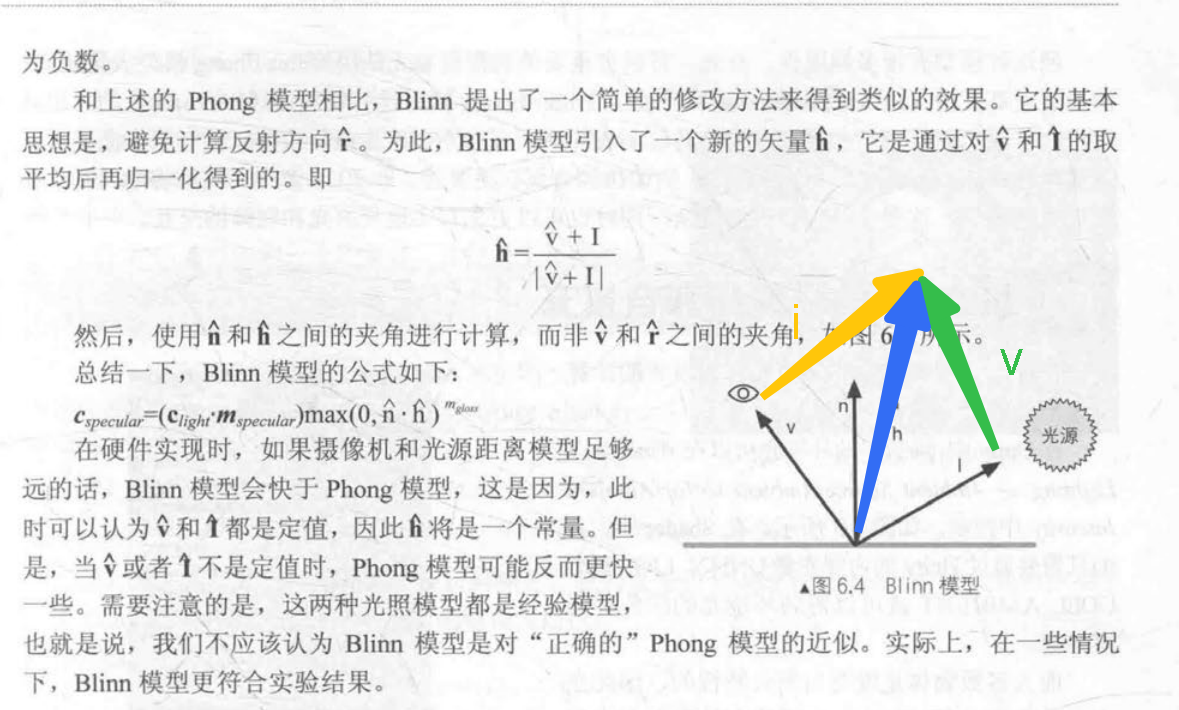
反射方向 = 2* dot(法线方向, 灯光方向)*法线方向 - 灯光方向
高光 = (高光颜色 * 灯光颜色) * max(0, pow(dot(摄像机方向, 反射方向), 光泽度) )

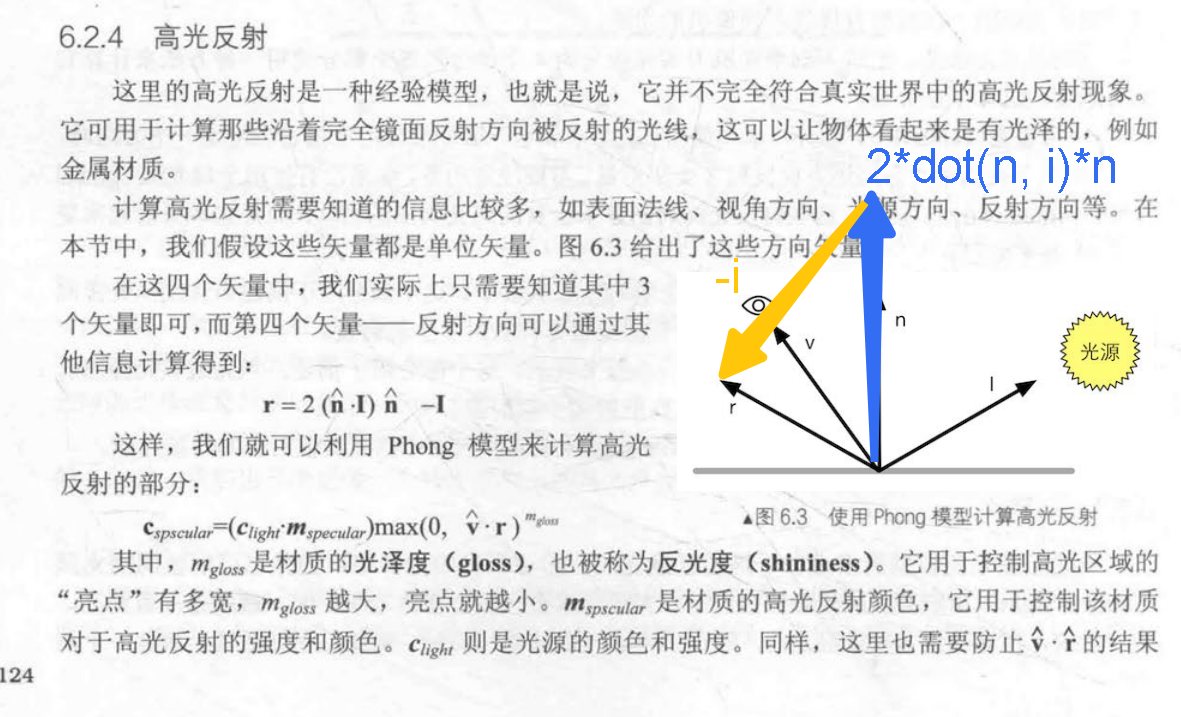
优化 反射方向计算
h = normal(摄像机方向 + 灯光方向)
高光 = (高光颜色 * 灯光颜色) * max(0, pow(dot(法线方向, h), 光泽度) )

Shader "Unity Shaders Book/Chapter 6/Blinn-Phong" {
Properties {
_Diffuse ("Diffuse", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_Specular ("Specular", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_Gloss ("Gloss", Range(8.0, 256)) = 20
}
SubShader {
Pass {
Tags { "LightMode"="ForwardBase" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "Lighting.cginc"
fixed4 _Diffuse;
fixed4 _Specular;
float _Gloss;
struct a2v {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
};
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float3 worldNormal : TEXCOORD0;
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD1;
};
v2f vert(a2v v) {
v2f o;
// Transform the vertex from object space to projection space
o.pos = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP, v.vertex);
// Transform the normal from object space to world space
o.worldNormal = mul(v.normal, (float3x3)_World2Object);
// Transform the vertex from object spacet to world space
o.worldPos = mul(_Object2World, v.vertex).xyz;
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target {
// Get ambient term
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz;
fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(i.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(_WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz);
// Compute diffuse term
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Diffuse.rgb * max(0, dot(worldNormal, worldLightDir));
// Get the view direction in world space
fixed3 viewDir = normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - i.worldPos.xyz);
// Get the half direction in world space
fixed3 halfDir = normalize(worldLightDir + viewDir);
// Compute specular term
fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(max(0, dot(worldNormal, halfDir)), _Gloss);
return fixed4(ambient + diffuse + specular, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Specular"
}
半兰伯特模型
phong的漫反射在没有环境光的情况下,明暗交界处会太黑。所以用半兰伯特可以提高暗部亮度。
漫反射 = (物体颜色 * 灯光颜色) * ( dot(法线方向, 灯光方向) * (_hartLambert) + (1 - _hartLambert)); // _hartLambert 默认是0.5
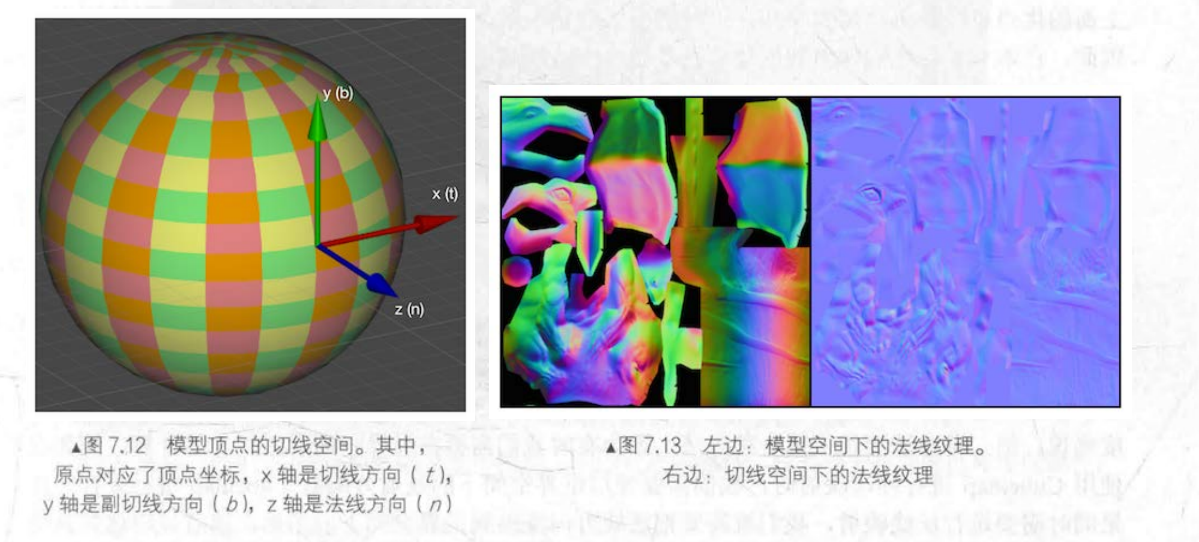
计算副切线 binormal
float3 binormal = cross( normalize(v.normal), normalize(v.tangent.xyz) ) * v.tangent.w;
v.tangent.w用于确定法线和切线的叉积后的方向
计算切线空间矩阵
// Declares 3x3 matrix 'rotation', filled with tangent space basis
#define TANGENT_SPACE_ROTATION \
float3 binormal = cross( normalize(v.normal), normalize(v.tangent.xyz) ) * v.tangent.w; \
float3x3 rotation = float3x3( v.tangent.xyz, binormal, v.normal )
法线解压缩
切线空间法线坐标轴
- z 法线方向 n
- x 切线方向 t
- y 副切线 binormal
inline fixed3 UnpackNormalDXT5nm (fixed4 packednormal)
{
fixed3 normal;
// 因为纹理存储的都是正数,所以需要反映射
normal.xy = packednormal.wy * 2 - 1;
// 因为单位法线整体模为1,length =sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z)。 点积可以用于计算向量长度dot(normal.xy, normal.xy)。所以求z就这样来的
normal.z = sqrt(1 - saturate(dot(normal.xy, normal.xy)));
return normal;
}
fixed4 packedNormal = tex2D(_BumpMap, i.uv.zw);
fixed3 tangentNormal;
// If the texture is not marked as "Normal map"
// tangentNormal.xy = (packedNormal.xy * 2 - 1) * _BumpScale;
// tangentNormal.z = sqrt(1.0 - saturate(dot(tangentNormal.xy, tangentNormal.xy)));
// Or mark the texture as "Normal map", and use the built-in funciton
tangentNormal = UnpackNormal(packedNormal);
// 缩放凹凸程度
tangentNormal.xy *= _BumpScale;
tangentNormal.z = sqrt(1.0 - saturate(dot(tangentNormal.xy, tangentNormal.xy)));

灰度图
某点的颜色为P(R,G,B),灰度计算方法:
- 浮点算法:Gray = R0.3+G0.59+B*0.11;
- 整数方法:Gray = (R30+G59+B*11)/100;
- 移位方法:Gray = (R76+G151+B*28)»8;
- 平均值法:Gray =(R+G+B)/3;
高度贴图
float4 Parallax (float4 texcoords, half3 viewDir)
{
#if !defined(_PARALLAXMAP) || (SHADER_TARGET < 30)
// Disable parallax on pre-SM3.0 shader target models
return texcoords;
#else
half h = tex2D (_ParallaxMap, texcoords.xy).g;
float2 offset = ParallaxOffset1Step (h, _Parallax, viewDir);
return float4(texcoords.xy + offset, texcoords.zw + offset);
#endif
}
#ifndef UNIVERSAL_PARALLAX_MAPPING_INCLUDED
#define UNIVERSAL_PARALLAX_MAPPING_INCLUDED
// 世界空间 视图方向 -> 切线空间 视图方向
// Return view direction in tangent space, make sure tangentWS.w is already multiplied by GetOddNegativeScale()
half3 GetViewDirectionTangentSpace(half4 tangentWS, half3 normalWS, half3 viewDirWS)
{
// must use interpolated tangent, bitangent and normal before they are normalized in the pixel shader.
half3 unnormalizedNormalWS = normalWS;
const half renormFactor = 1.0 / length(unnormalizedNormalWS);
// use bitangent on the fly like in hdrp
// IMPORTANT! If we ever support Flip on double sided materials ensure bitangent and tangent are NOT flipped.
half crossSign = (tangentWS.w > 0.0 ? 1.0 : -1.0); // we do not need to multiple GetOddNegativeScale() here, as it is done in vertex shader
half3 bitang = crossSign * cross(normalWS.xyz, tangentWS.xyz);
half3 WorldSpaceNormal = renormFactor * normalWS.xyz; // we want a unit length Normal Vector node in shader graph
// to preserve mikktspace compliance we use same scale renormFactor as was used on the normal.
// This is explained in section 2.2 in "surface gradient based bump mapping framework"
half3 WorldSpaceTangent = renormFactor * tangentWS.xyz;
half3 WorldSpaceBiTangent = renormFactor * bitang;
half3x3 tangentSpaceTransform = half3x3(WorldSpaceTangent, WorldSpaceBiTangent, WorldSpaceNormal);
half3 viewDirTS = mul(tangentSpaceTransform, viewDirWS);
return viewDirTS;
}
#ifndef BUILTIN_TARGET_API
half2 ParallaxOffset1Step(half height, half amplitude, half3 viewDirTS)
{
height = height * amplitude - amplitude / 2.0;
half3 v = normalize(viewDirTS);
v.z += 0.42;
return height * (v.xy / v.z);
}
#endif
//
float2 ParallaxMapping(TEXTURE2D_PARAM(heightMap, sampler_heightMap), half3 viewDirTS, half scale, float2 uv)
{
half h = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(heightMap, sampler_heightMap, uv).g;
float2 offset = ParallaxOffset1Step(h, scale, viewDirTS);
return offset;
}
#endif // UNIVERSAL_PARALLAX_MAPPING_INCLUDED
void ApplyPerPixelDisplacement(half3 viewDirTS, inout float2 uv)
{
#if defined(_PARALLAXMAP)
uv += ParallaxMapping(TEXTURE2D_ARGS(_ParallaxMap, sampler_ParallaxMap), viewDirTS, _Parallax, uv);
#endif
}
half4 LitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_Target
{
#if defined(_PARALLAXMAP)
#if defined(REQUIRES_TANGENT_SPACE_VIEW_DIR_INTERPOLATOR)
half3 viewDirTS = input.viewDirTS;
#else
half3 viewDirWS = GetWorldSpaceNormalizeViewDir(input.positionWS);
half3 viewDirTS = GetViewDirectionTangentSpace(input.tangentWS, input.normalWS, viewDirWS);
#endif
ApplyPerPixelDisplacement(viewDirTS, input.uv);
#endif
...
}
透明混合

解决半透明 深度问题
问题:


Shader "Unity Shaders Book/Chapter 8/Alpha Blending With ZWrite" {
Properties {
_Color ("Color Tint", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_MainTex ("Main Tex", 2D) = "white" {}
_AlphaScale ("Alpha Scale", Range(0, 1)) = 1
}
SubShader {
Tags {"Queue"="Transparent" "IgnoreProjector"="True" "RenderType"="Transparent"}
// Extra pass that renders to depth buffer only
Pass {
ZWrite On
ColorMask 0
}
Pass {
Tags { "LightMode"="ForwardBase" }
ZWrite Off
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "Lighting.cginc"
fixed4 _Color;
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
fixed _AlphaScale;
struct a2v {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 texcoord : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float3 worldNormal : TEXCOORD0;
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD1;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD2;
};
v2f vert(a2v v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _MainTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target {
fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(i.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(i.worldPos));
fixed4 texColor = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
fixed3 albedo = texColor.rgb * _Color.rgb;
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz * albedo;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * albedo * max(0, dot(worldNormal, worldLightDir));
return fixed4(ambient + diffuse, texColor.a * _AlphaScale);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Transparent/VertexLit"
}
阴影
使用了屏幕空间的阴影映射技术时:
- Unity 首先会通过调用 LightMode ShadowCaster Pass 来得到可投射阴影的光源的阴影映射纹理以及摄像机的深度纹理。
- 然后,根据光源的阴影映射 纹理和摄像机的深度纹理来得到屏幕空间的阴影图。
- 如果摄像机的深度图中记录的表面深度大于转换到阴影映射纹理中的深度值,就说明该表面虽然是可见的,但是却处千该光源的阴影中。通过这 样的方式,阴影图就包含了屏幕空间中所有有阴影的区域。
- 如果我们想要这个物体接收来自其他物体的阴影,只需要在 Shader 中对阴影图进行采样。
- 由于阴影图是屏幕空间下的,因此,我们首先需要把表面坐标从模型空间变换到屏幕空间中,然后使用这个坐标对阴影图进行采样即可。
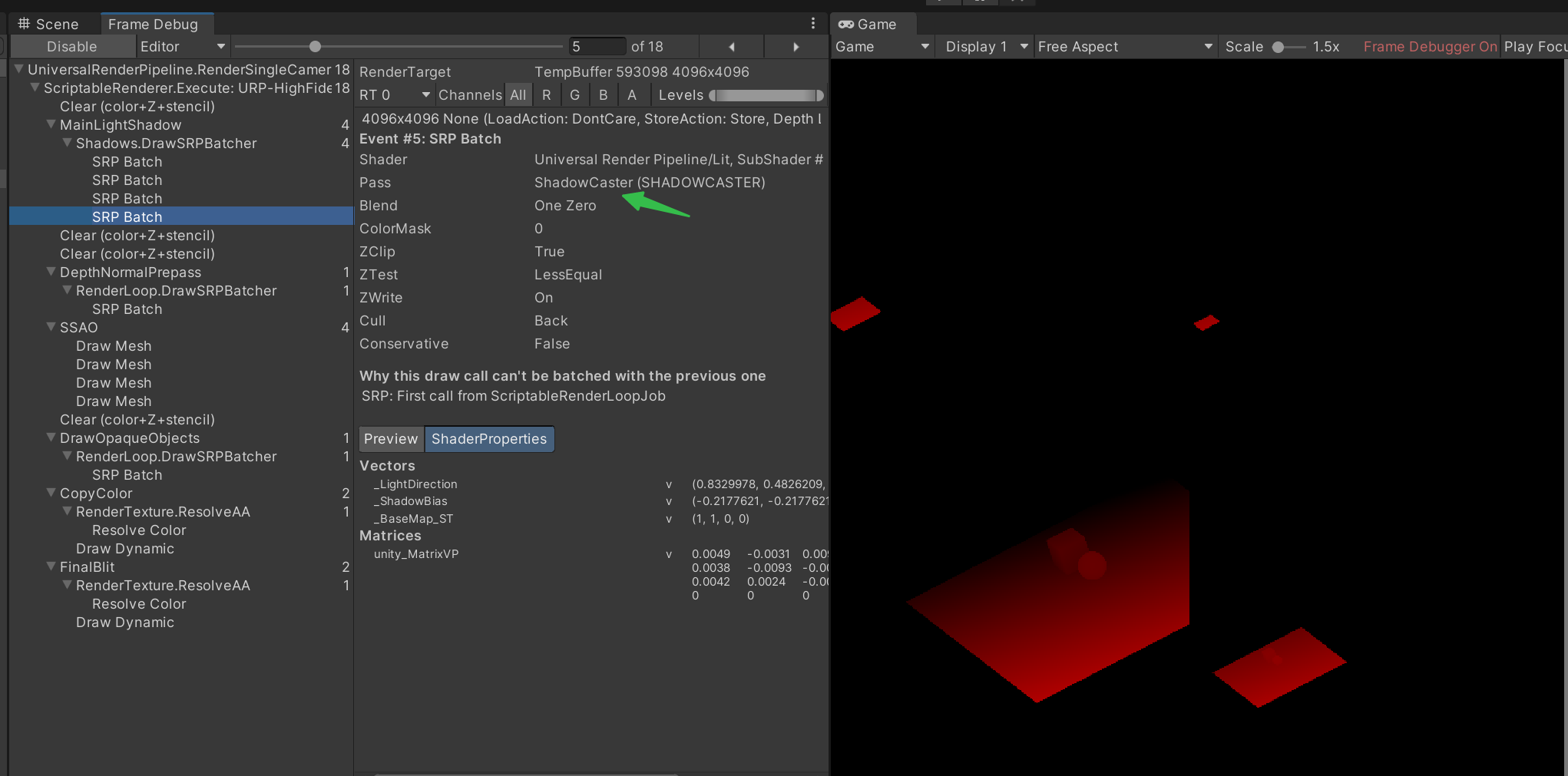
渲染投影贴图
以灯光为摄像机视角,渲染 Tags { “LightMode” = “ShadowCaster” } 的Pass。得到灯光视角深度图。_MainLightShadowmapTexture (URP)或者__ShadowmapTexture (内置渲染管线)
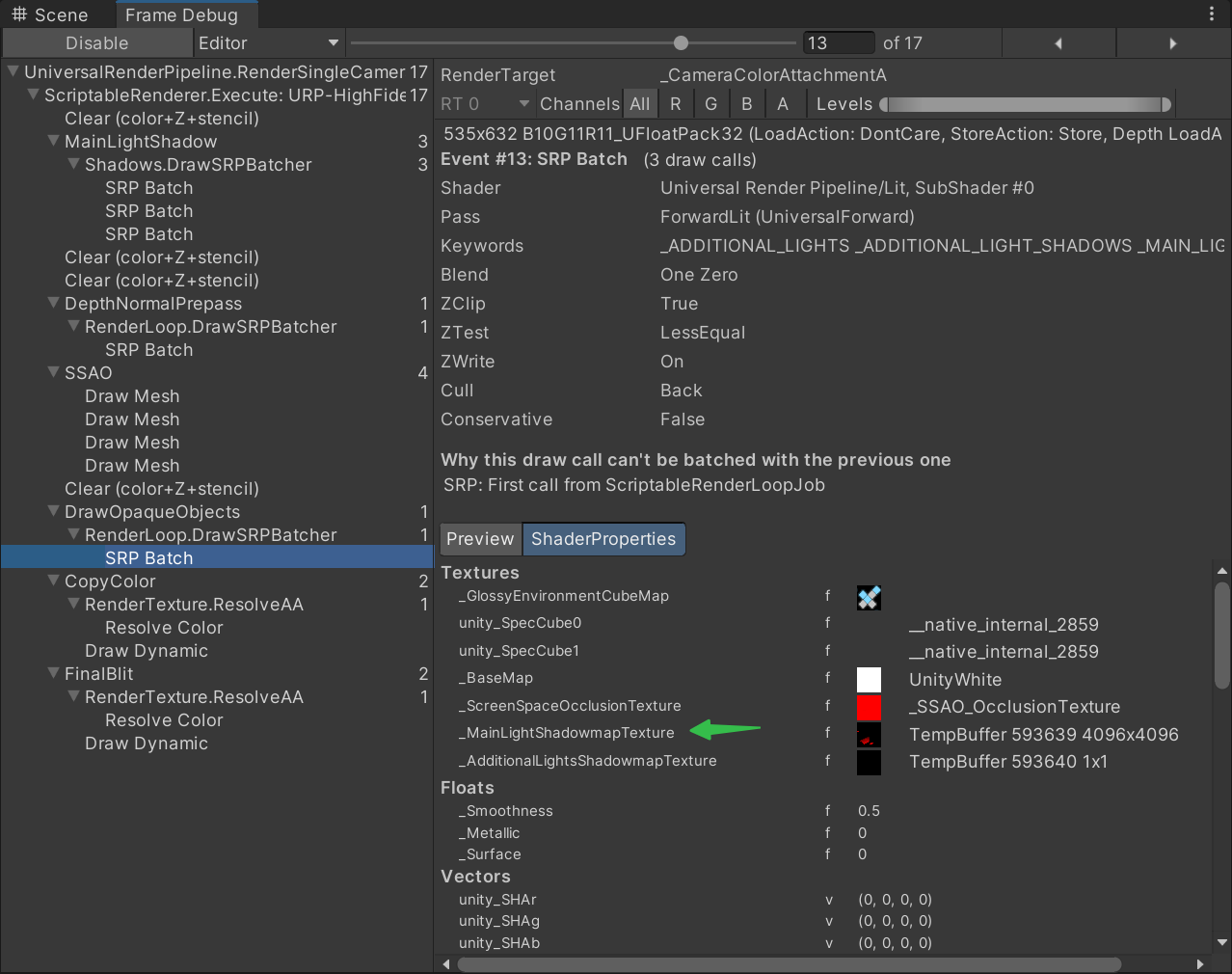
平面空间 投影贴图
在内置渲染管线中会通过ScreenSpaceShadows.shader 将生成平面空间投影贴图
- 根据归一化设备空间坐标、深度、unity_MatrixInvVP,获取世界空间位置
- 将世界空间位置转换成阴影投影空间位置
- 用阴影投影空间位置 取采样 阴影投影深度贴图
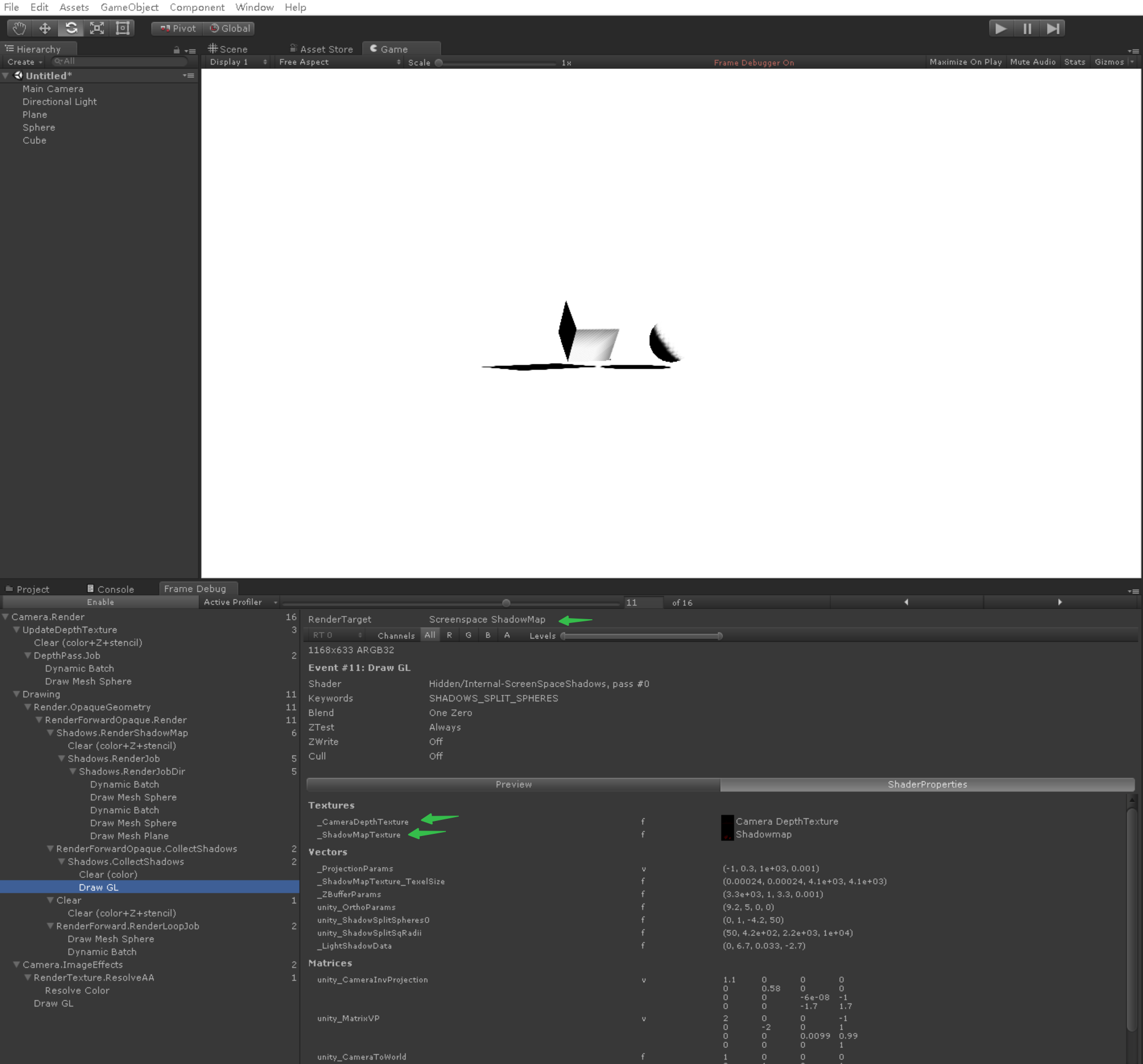
half4 Fragment(Varyings input) : SV_Target
{
UNITY_SETUP_STEREO_EYE_INDEX_POST_VERTEX(input);
// 以归一化设备空间为uv,获取摄像机深度贴图中的深度
#if UNITY_REVERSED_Z
float deviceDepth = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_X(_CameraDepthTexture, sampler_PointClamp, input.texcoord.xy).r;
#else
float deviceDepth = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_X(_CameraDepthTexture, sampler_PointClamp, input.texcoord.xy).r;
deviceDepth = deviceDepth * 2.0 - 1.0;
#endif
// 根据归一化设备空间坐标和深度,获取世界空间位置
//Fetch shadow coordinates for cascade.
float3 wpos = ComputeWorldSpacePosition(input.texcoord.xy, deviceDepth, unity_MatrixInvVP);
// 将世界空间位置转换成阴影投影空间位置
float4 coords = TransformWorldToShadowCoord(wpos);
// 计算阴影
// Screenspace shadowmap is only used for directional lights which use orthogonal projection.
half realtimeShadow = MainLightRealtimeShadow(coords);
return realtimeShadow;
}
// 根据归一化设备空间坐标和深度,获取世界空间位置
float3 ComputeWorldSpacePosition(float2 positionNDC, float deviceDepth, float4x4 invViewProjMatrix)
{
// 根据归一化设备空间坐标和深度,获取齐次裁剪空间位置
float4 positionCS = ComputeClipSpacePosition(positionNDC, deviceDepth);
// 齐次裁剪空间位置 转 世界空间位置
float4 hpositionWS = mul(invViewProjMatrix, positionCS);
return hpositionWS.xyz / hpositionWS.w;
}
// 根据归一化设备空间坐标和深度,获取齐次裁剪空间位置
float4 ComputeClipSpacePosition(float2 positionNDC, float deviceDepth)
{
float4 positionCS = float4(positionNDC * 2.0 - 1.0, deviceDepth, 1.0);
#if UNITY_UV_STARTS_AT_TOP
// Our world space, view space, screen space and NDC space are Y-up.
// Our clip space is flipped upside-down due to poor legacy Unity design.
// The flip is baked into the projection matrix, so we only have to flip
// manually when going from CS to NDC and back.
positionCS.y = -positionCS.y;
#endif
return positionCS;
}
// 将世界空间位置转换成阴影投影空间位置
float4 TransformWorldToShadowCoord(float3 positionWS)
{
#ifdef _MAIN_LIGHT_SHADOWS_CASCADE
half cascadeIndex = ComputeCascadeIndex(positionWS);
#else
half cascadeIndex = half(0.0);
#endif
float4 shadowCoord = mul(_MainLightWorldToShadow[cascadeIndex], float4(positionWS, 1.0));
return float4(shadowCoord.xyz, 0);
}
half MainLightRealtimeShadow(float4 shadowCoord)
{
#if !defined(MAIN_LIGHT_CALCULATE_SHADOWS)
return half(1.0);
#elif defined(_MAIN_LIGHT_SHADOWS_SCREEN) && !defined(_SURFACE_TYPE_TRANSPARENT)
return SampleScreenSpaceShadowmap(shadowCoord);
#else
ShadowSamplingData shadowSamplingData = GetMainLightShadowSamplingData();
half4 shadowParams = GetMainLightShadowParams();
return SampleShadowmap(TEXTURE2D_ARGS(_MainLightShadowmapTexture, sampler_LinearClampCompare), shadowCoord, shadowSamplingData, shadowParams, false);
#endif
}
ShadowSamplingData GetMainLightShadowSamplingData()
{
ShadowSamplingData shadowSamplingData;
// shadowOffsets are used in SampleShadowmapFiltered for low quality soft shadows.
shadowSamplingData.shadowOffset0 = _MainLightShadowOffset0;
shadowSamplingData.shadowOffset1 = _MainLightShadowOffset1;
// shadowmapSize is used in SampleShadowmapFiltered otherwise
shadowSamplingData.shadowmapSize = _MainLightShadowmapSize;
shadowSamplingData.softShadowQuality = _MainLightShadowParams.y;
return shadowSamplingData;
}
// ShadowParams
// x: ShadowStrength
// y: 1.0 if shadow is soft, 0.0 otherwise
half4 GetMainLightShadowParams()
{
return _MainLightShadowParams;
}
real SampleShadowmap(TEXTURE2D_SHADOW_PARAM(ShadowMap, sampler_ShadowMap), float4 shadowCoord, ShadowSamplingData samplingData, half4 shadowParams, bool isPerspectiveProjection = true)
{
// //只要在编译时知道isPerspectiveProjection,编译器就会优化这个分支
// Compiler will optimize this branch away as long as isPerspectiveProjection is known at compile time
if (isPerspectiveProjection)
shadowCoord.xyz /= shadowCoord.w;
real attenuation;
real shadowStrength = shadowParams.x;
// Quality levels are only for platforms requiring strict static branches
#if defined(_SHADOWS_SOFT_LOW)
attenuation = SampleShadowmapFilteredLowQuality(TEXTURE2D_SHADOW_ARGS(ShadowMap, sampler_ShadowMap), shadowCoord, samplingData);
#elif defined(_SHADOWS_SOFT_MEDIUM)
attenuation = SampleShadowmapFilteredMediumQuality(TEXTURE2D_SHADOW_ARGS(ShadowMap, sampler_ShadowMap), shadowCoord, samplingData);
#elif defined(_SHADOWS_SOFT_HIGH)
attenuation = SampleShadowmapFilteredHighQuality(TEXTURE2D_SHADOW_ARGS(ShadowMap, sampler_ShadowMap), shadowCoord, samplingData);
#elif defined(_SHADOWS_SOFT)
if (shadowParams.y > SOFT_SHADOW_QUALITY_OFF)
{
attenuation = SampleShadowmapFiltered(TEXTURE2D_SHADOW_ARGS(ShadowMap, sampler_ShadowMap), shadowCoord, samplingData);
}
else
{
attenuation = real(SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_SHADOW(ShadowMap, sampler_ShadowMap, shadowCoord.xyz));
}
#else
attenuation = real(SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_SHADOW(ShadowMap, sampler_ShadowMap, shadowCoord.xyz));
#endif
attenuation = LerpWhiteTo(attenuation, shadowStrength);
//从光锥体积中掉出来的阴影坐标必须始终返回衰减1.0
//TODO:我们可以在这里使用branch在某些平台上保存一些性能。
// Shadow coords that fall out of the light frustum volume must always return attenuation 1.0
// TODO: We could use branch here to save some perf on some platforms.
return BEYOND_SHADOW_FAR(shadowCoord) ? 1.0 : attenuation;
}
real LerpWhiteTo(real b, real t)
{
real oneMinusT = 1.0 - t;
return oneMinusT + b * t;
}
#define SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_SHADOW(textureName, samplerName, coord3) textureName.SampleCmpLevelZero(samplerName, (coord3).xy, (coord3).z)
#define BEYOND_SHADOW_FAR(shadowCoord) shadowCoord.z <= 0.0 || shadowCoord.z >= 1.0
接收显示阴影
half4 ForwardLitPassFragment (Varyings i) : SV_Target
{
...
// 在主Pass,将世界空间顶点位置转成投影空间位置
float4 shadowCoord = TransformWorldToShadowCoord(i.positionWS);
// 内部会取获取阴影衰减,阴影衰减就是通过采样阴影贴图纹理得到的
Light light = GetMainLight(shadowCoord);
half3 lightDir = light.direction;
half3 lightColor = light.color * light.distanceAttenuation * light.shadowAttenuation;
half3 realtimeLight = LightingLambert(lightColor, lightDir, i.normalWS);
half4 shading = half4(backGI + realtimeLight, 1);
half4 albedo = shading + col * i.color;
return albedo;
}
struct Light
{
half3 direction;
half3 color;
float distanceAttenuation; // full-float precision required on some platforms
half shadowAttenuation;
uint layerMask;
};
// 获取灯光信息
Light GetMainLight(float4 shadowCoord)
{
Light light = GetMainLight();
light.shadowAttenuation = MainLightRealtimeShadow(shadowCoord);
return light;
}
// 灯光阴影
half MainLightShadow(float4 shadowCoord, float3 positionWS, half4 shadowMask, half4 occlusionProbeChannels)
{
half realtimeShadow = MainLightRealtimeShadow(shadowCoord);
#ifdef CALCULATE_BAKED_SHADOWS
half bakedShadow = BakedShadow(shadowMask, occlusionProbeChannels);
#else
half bakedShadow = half(1.0);
#endif
#ifdef MAIN_LIGHT_CALCULATE_SHADOWS
half shadowFade = GetMainLightShadowFade(positionWS);
#else
half shadowFade = half(1.0);
#endif
return MixRealtimeAndBakedShadows(realtimeShadow, bakedShadow, shadowFade);
}
half MainLightRealtimeShadow(float4 shadowCoord)
{
#if !defined(MAIN_LIGHT_CALCULATE_SHADOWS)
return half(1.0);
#elif defined(_MAIN_LIGHT_SHADOWS_SCREEN) && !defined(_SURFACE_TYPE_TRANSPARENT)
return SampleScreenSpaceShadowmap(shadowCoord);
#else
ShadowSamplingData shadowSamplingData = GetMainLightShadowSamplingData();
half4 shadowParams = GetMainLightShadowParams();
return SampleShadowmap(TEXTURE2D_ARGS(_MainLightShadowmapTexture, sampler_LinearClampCompare), shadowCoord, shadowSamplingData, shadowParams, false);
#endif
}
half MixRealtimeAndBakedShadows(half realtimeShadow, half bakedShadow, half shadowFade)
{
#if defined(LIGHTMAP_SHADOW_MIXING)
return min(lerp(realtimeShadow, 1, shadowFade), bakedShadow);
#else
return lerp(realtimeShadow, bakedShadow, shadowFade);
#endif
}
half GetMainLightShadowFade(float3 positionWS)
{
float3 camToPixel = positionWS - _WorldSpaceCameraPos;
float distanceCamToPixel2 = dot(camToPixel, camToPixel);
float fade = saturate(distanceCamToPixel2 * float(_MainLightShadowParams.z) + float(_MainLightShadowParams.w));
return half(fade);
}
float4 _MainLightShadowOffset0; // xy: offset0, zw: offset1
float4 _MainLightShadowOffset1; // xy: offset2, zw: offset3
float4 _MainLightShadowParams; // (x: shadowStrength, y: >= 1.0 if soft shadows, 0.0 otherwise, z: main light fade scale, w: main light fade bias)
float4 _MainLightShadowmapSize; // (xy: 1/width and 1/height, zw: width and height)
深度和法线纹理
- 被存储在一张纹理中,深度纹理里的深度值范围是[O, l], 而且通常是非线性分布 的
- 这些深度值来自于顶点变换后得到的归一化的设备坐标 (Normalized Device Coordinates , NDC) 。
- 需要把它的顶点从 模型空间变换到齐次裁剪坐标系下,这是通过在顶点着色器中乘以 MVP 变换矩阵得到的 。
- 在变换的最后一步,我们需要使用一个投影矩阵来变换顶点, 当我们使用的是透视投影类型的摄像机 时,这个投影矩阵就是非线性的。
- 在得到 NDC 后,深度纹理中的像素值就可以很方便地计算得到了,这些深度值就对应了 NDC 中顶点坐标的 分量的值。由于 NDC 分量的范围在[-1, I], 为了让这些值能够存储在一张图 像中,我们需要使用下面的公式对其进行映射:
- 像素深度=归一化设备空间深度值 * 0.5 + 0.5
深度纹理值的转换过程如下
齐次裁剪坐标 = mul(MVP, 模型空间顶点位置);
齐次裁剪坐标 [-1, 1] -> 像素值 [0, 1]

Unity如何获得
- 设置Camera的depthTextureMode
- unity会把每个拥有Pass { Tags { “LightMode” = “ShadowCaster” } } 渲染
- 然后shader就可以通过sampler2D _CameraDepthTexture;或者sampler2D _CameraDepthNormalsTexture;来访问
- _CameraDepthNormalsTexture.xy 是法线值
- _CameraDepthNormalsTexture.wz 是深度值
// 开启深度纹理 渲染贴图是 _CameraDepthTexture
GetComponent<Camera>().depthTextureMode |= DepthTextureMode.Depth;
// 开启深度和法线纹理 渲染贴图是 _CameraDepthNormalsTexture
GetComponent<Camera>().depthTextureMode |= DepthTextureMode.DepthNormals;



// Z buffer to linear 0..1 depth
inline float Linear01Depth( float z )
{
return 1.0 / (_ZBufferParams.x * z + _ZBufferParams.y);
}
// Z buffer to linear depth
inline float LinearEyeDepth( float z )
{
return 1.0 / (_ZBufferParams.z * z + _ZBufferParams.w);
}
# define SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(sampler, uv) (tex2D(sampler, uv).r)
# define SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE_PROJ(sampler, uv) (tex2Dproj(sampler, uv).r)
# define SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE_LOD(sampler, uv) (tex2Dlod(sampler, uv).r)
// Encoding/decoding [0..1) floats into 8 bit/channel RG. Note that 1.0 will not be encoded properly.
inline float2 EncodeFloatRG( float v )
{
float2 kEncodeMul = float2(1.0, 255.0);
float kEncodeBit = 1.0/255.0;
float2 enc = kEncodeMul * v;
enc = frac (enc);
enc.x -= enc.y * kEncodeBit;
return enc;
}
inline float DecodeFloatRG( float2 enc )
{
float2 kDecodeDot = float2(1.0, 1/255.0);
return dot( enc, kDecodeDot );
}
// Encoding/decoding view space normals into 2D 0..1 vector
inline float2 EncodeViewNormalStereo( float3 n )
{
float kScale = 1.7777;
float2 enc;
enc = n.xy / (n.z+1);
enc /= kScale;
enc = enc*0.5+0.5;
return enc;
}
inline float3 DecodeViewNormalStereo( float4 enc4 )
{
float kScale = 1.7777;
float3 nn = enc4.xyz*float3(2*kScale,2*kScale,0) + float3(-kScale,-kScale,1);
float g = 2.0 / dot(nn.xyz,nn.xyz);
float3 n;
n.xy = g*nn.xy;
n.z = g-1;
return n;
}
inline float4 EncodeDepthNormal( float depth, float3 normal )
{
float4 enc;
enc.xy = EncodeViewNormalStereo (normal);
enc.zw = EncodeFloatRG (depth);
return enc;
}
inline void DecodeDepthNormal( float4 enc, out float depth, out float3 normal )
{
depth = DecodeFloatRG (enc.zw);
normal = DecodeViewNormalStereo (enc);
}
深度纹理重建像素对应的世界位置
原理:利用深度纹理和当前帧的视角*投影矩阵的逆矩阵来求得当前像素在世界空间的坐标。
屏幕后处理根据深度纹理构建每个像素在世界空间的位置_深度空间贴图-CSDN博客
根据深度信息重建世界坐标_后处理中,如果根据深度缓存还原出世界坐标?-CSDN博客
//main problem encountered is camera.projectionMatrix = ??????? worked but further from camera became more inaccurate
//had to use GL.GetGPUProjectionMatrix( ) seems to stay pretty exact now
//in script somewhere:
Matrix4x4 viewMat = camera.worldToCameraMatrix;
Matrix4x4 projMat = GL.GetGPUProjectionMatrix( camera.projectionMatrix, false );
Matrix4x4 viewProjMat = (projMat * viewMat);
Shader.SetGlobalMatrix("_ViewProjInv", viewProjMat.inverse);
//in fragment shader:
uniform float4x4 _ViewProjInv;
float4 GetWorldPositionFromDepth( float2 uv_depth )
{
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture, uv_depth);
float4 H = float4(uv_depth.x*2.0-1.0, (uv_depth.y)*2.0-1.0, depth, 1.0);
float4 D = mul(_ViewProjInv,H);
return D/D.w;
}
// Get the depth buffer value at this pixel.
//从深度纹理图中得到当前像素点的深度,这个深度是非线性的深度
//对于Zndc首先他不是一个线性的,为了得到z01,也就是线性的,我们需要使用Linear01Depth函数对于Zndc计算得到线性的d。
float d = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture, i.uv_depth);
// H is the viewport position at this pixel in the range -1 to 1.
//NDC和深度纹理图中的像素深度对应关系是:
//d=0.5*Zndc+0.5;
//(NDC坐标是处于(-1,1),但是深度纹理图中的深度的范围是处于(0,1)之间的)
//要想得到视角坐标系下的NDC坐标,首先我们要明确NDC坐标的范围[-1,1],由上面的公式我们可以得到NDC坐标中的z坐标,但是x和y坐标,我们就需要从像素的纹理坐标得到也就是i.uv中的x和y坐标,但是对于x和y坐标的范围是[0,1]。
float4 H = float4(i.uv.x * 2 - 1, i.uv.y * 2 - 1, d * 2 - 1, 1);
// Transform by the view-projection inverse.
//currentViewProjectionMatrix = camera.projectionMatrix * camera.worldToCameraMatrix;
//Matrix4x4 currentViewProjectionInverseMatrix = currentViewProjectionMatrix.inverse;
//使用当前帧的视角,投影矩阵的逆矩阵对其进行变换。
float4 D = mul(_CurrentViewProjectionInverseMatrix, H);
// Divide by w to get the world position.
//最后将得到的结果除以w分量得到世界空间下的坐标。
float4 worldPos = D / D.w;